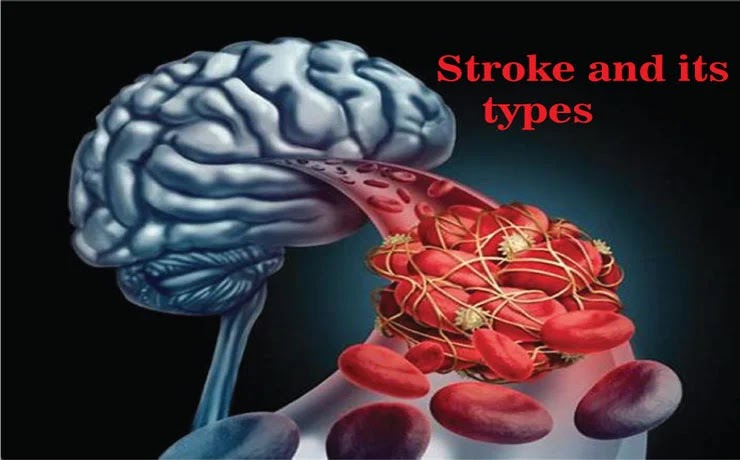
What is Stroke and What are its Different Types?
A stroke, also known as a “cerebrovascular accident” (CVAC) is an abrupt disruption of blood supply to the brain that results in destruction of tissues. The consequence of this destruction is impairment of neurological functions and other secondary effects. A stroke can either be acute or chronic. Acute stroke is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately. It happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts or bleeds and stops supplying blood to the affected area, resulting in tissue death. It can be either ischemic or hemorrhagic. A hemorrhagic stroke is caused by bleeding in the brain instead of a blocked artery, which is called an Ischemic stroke. Let us explore further details about these two subtypes of strokes with sub-types as well
What is Ischemic Stroke?
Ischemic stroke occurs when an artery blocked by clots or cholesterol becomes so narrow that it can no longer deliver blood to the brain. Cells in the brain need a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients delivered by the blood, but during a stroke, the blood flow is cut off, causing the cells to die. These cells are responsible for functions like memory and language, so if they’re damaged or die, you may experience problems with your ability to think, move, and communicate.It can cause serious long-term disability or death if it’s left untreated. Ischemic stroke can be either acute or chronic.
Acute Ischemic Stroke
An acute ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot blocks one of the arteries that brings blood to the brain. It can cause a lot of damage very quickly, since the brain doesn’t have a way to repair itself when it’s not getting blood. An acute ischemic stroke can be fatal if immediate medical treatment isn’t received. Some warning signs of an acute ischemic stroke include: Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or problems understanding Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg that doesn’t go away, even when you’ve had a minor injury or are sick.
Chronic Ischemic Stroke
A chronic ischemic stroke happens when the arteries that bring blood to the brain become narrowed and hardened, which increases the risk of blood clots. Doctors don’t know why this happens in some people and not others, but they do know that some people are at a higher risk, like people with high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, high cholesterol, or a family history of heart disease. Chronic ischemic strokes are less sudden than acute ischemic strokes, but can still cause serious damage if they aren’t treated right away. Chronic ischemic strokes can also lead to blood clots and cause atrial fibrillation.
What is Hemorrhagic Stroke?
Hemorrhagic strokes are caused by bleeding in the brain, often from ruptured blood vessels, rather than blocked arteries like ischemic strokes do. A hemorrhagic stroke is also called a bleed stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, or intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Bleeding in the brain can be caused by a number of things, like an aneurysm or other malformation, a vascular malformation, a traumatic brain injury, or a bleed in the brain due to cancer. Hemorrhagic strokes cause a larger amount of tissue damage than ischemic strokes, and they’re also more likely to cause death. They’re also more likely to cause long-term disability than ischemic strokes.
Sub-types of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Intracerebral hemorrhage:
This is bleeding that happens inside the brain tissue itself.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage:
Bleeding occurs between the brain and its outer covering (the meninges). This type of bleeding usually creates a sudden headache and is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Subdural hemorrhage:
This occurs when blood collects between the skull and the outer covering of the brain.
Extradural hemorrhage:
This is bleeding that happens outside of the brain and the skull.
Cerebral venous thrombosis:
This is rare and happens when blood clots form in the veins that drain the brain.
Intracerebral hemorrhage:
This is a combination of intracerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Concluding Words
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing cells in the brain to die. There are two main types of strokes: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. An ischemic stroke happens when a blood vessel is blocked, while a hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures. There are sub-types of strokes, such as intra-cerebral, subarachnoid, subdural, extradural, cerebral venous thrombosis, and intracerebral hemorrhage.













Very informative topic keep it up❤
ReplyDelete